SRAM
SRAM is the second generation synchronous reluctance motor, which provides high efficiency and peak power in the whole operating range. SRAM can provide any size as required, which is a special balance. Because it does not contain rare earth elements, it has the characteristics of high performance and low cost.
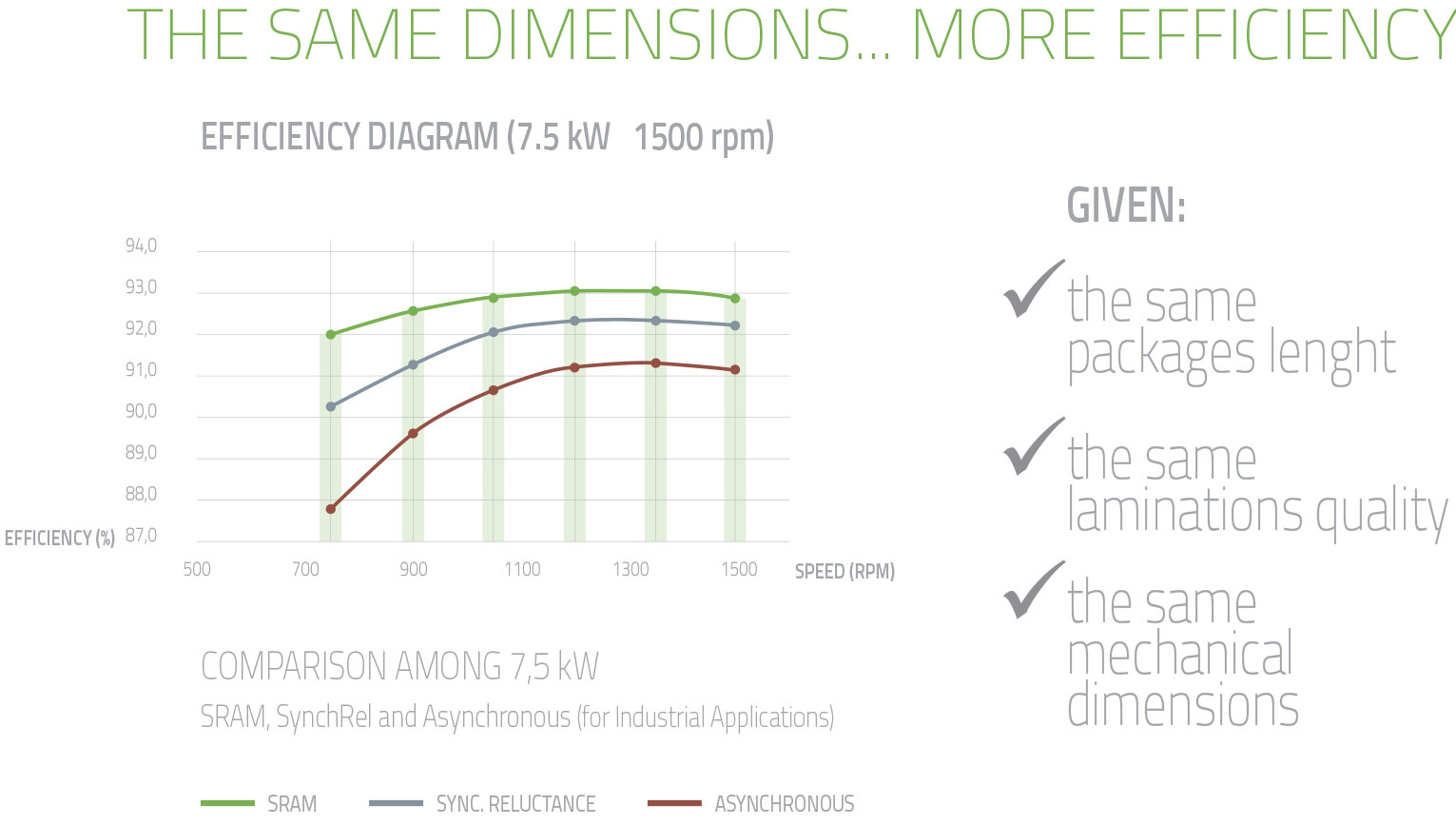
Efficiency: Although asynchronous and synchronous motors have the same size and cost, SRAM achieves higher efficiency, especially in part of the load range. Compared with permanent magnet motor, although permanent magnet motor achieves the maximum peak efficiency, SRAM achieves higher efficiency in the whole working range.
Leadership 3 times: SRAM further reduces losses by 4 times 20% (compared with the newly released IE4 specifications - 20%, IE5 and IE6 - 20% in the future, and even IE7 - 20% in the future), which may make it conform to the unpublished and future IE8 efficiency specifications.
Cost-effectiveness: Through SRAM design, the cost of active materials can be reduced by 30%, more compact motors (smaller size), and ferrite magnets with sustainability and lower cost.
High overload and wide magnetic field weakening: SRAM achieves extended overload at any speed. In addition, it provides high torque partial load and high power full load, which is characterized by ultra-wide field braiding up to 10:1. All of these, with very low torque fluctuations, have so far been unparalleled.
SRAM motor with its high performance Sensorless control, without any decomposer or encoder can ensure excellent positioning and speed accuracy.








 Address:Rm. 508-509, Tower A - ShangJi Information Building, No. 1588 Lianhang Rd., Minhang Dist., Shanghai
Address:Rm. 508-509, Tower A - ShangJi Information Building, No. 1588 Lianhang Rd., Minhang Dist., Shanghai Tel:86-21-54320326
Tel:86-21-54320326  Fax:86-21-54320325
Fax:86-21-54320325  Email:magtek@magteksh.com
Email:magtek@magteksh.com
